Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Arai, Yosuke*; Kuroda, Kenta*; Nomoto, Takuya*; Kurokawa, Kifu*; Shin, S.*; Kubota, Masato; Haga, Yoshinori; Suzuki, Hiroyuki*; Iwasa, Kazuaki*; Arita, Ryotaro*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tokunaga, Yo; Aoki, Dai*; Braithwaite, D.*; Knebel, G.*; Brison, J.-P.*; Pourret, A.*; Lapertot, G.*; Niu, Q.*; Valiska, M.*; Flouquet, J.*; et al.
no journal, ,
Recently, uniaxial stress has been found to be a remarkable tool for tuning the pairing strength in a ferromagnetic superconductor URhGe. A relatively small uniaxial stress applied along the  crystal axis changes the superconducting (SC) phase diagram significantly, merging the low-field SC and reentrant SC domes, with a large enhancement of
crystal axis changes the superconducting (SC) phase diagram significantly, merging the low-field SC and reentrant SC domes, with a large enhancement of 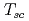 . The
. The 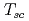 increases both at zero field and under a field, reaching 1 K, more than twice higher than at ambient pressure. This enhancement of SC has been shown to be directly related to a change of the magnetic dimensionality, moving the system away from the Ising-type limit, which results in the rapid decrease of the
increases both at zero field and under a field, reaching 1 K, more than twice higher than at ambient pressure. This enhancement of SC has been shown to be directly related to a change of the magnetic dimensionality, moving the system away from the Ising-type limit, which results in the rapid decrease of the 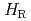 . In this study, by means of zero-field
. In this study, by means of zero-field 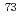 Ge NMR in the ferromagnetic state, we have investigated the effects of uniaxial stress on the electronic state of URhGe.
Ge NMR in the ferromagnetic state, we have investigated the effects of uniaxial stress on the electronic state of URhGe.
Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro; Hosaka, Atsushi; Takeuchi, Sachiko*; Takizawa, Makoto*
no journal, ,
Recently, the exotic hadrons considered to be a pentaquark have been reported in the LHCb experiments. In this talk, we study the 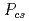 states as the hadronic molecule of a heavy meson and heavy baryon, where the pseudoscalar-meson exchange potential and the coupling to the compact five-quark states are introduced. We compute an energy and a decay width, and discuss a role of the interactions introduced.
states as the hadronic molecule of a heavy meson and heavy baryon, where the pseudoscalar-meson exchange potential and the coupling to the compact five-quark states are introduced. We compute an energy and a decay width, and discuss a role of the interactions introduced.
Harada, Hiroyuki; Saha, P. K.; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*; Fuchi, Aoi*; Shibata, Takanori*; Kinsho, Michikazu
no journal, ,
The high-intensity proton accelerator adopts a charge exchange injection scheme, which injects with exchanging from negative Hydrogen ion to proton by using carbon foil. This scheme is destructive-type method by using the foil and can accumulate high intensity proton beam. However, the uncontrolled beam losses by scattering at the foil and the foil breaking by the beam collision are a key issue of high-intensity proton accelerator in the world. In the J-PARC, we newly propose a laser stripping injection scheme of nondestructive-type method as an alternative to the foil and are under development for a proof-of-principle experiment of the method. In my presentation, we introduce an overview of laser stripping injection. Additionally, we report the status of the development and the results of the first experiment (day-1).
 V
V O
O in transverse magnetic fields
in transverse magnetic fieldsOnishi, Hiroaki; Mori, Michiyasu; Okutani, Akira*; Kimura, Shojiro*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 MnGa films
MnGa filmsSumida, Kazuki; Sakuraba, Yuya*; Masuda, Keisuke*; Kono, Takashi*; Kakoki, Masaaki*; Goto, Kazuki*; Zhou, W.*; Miyamoto, Koji*; Miura, Yoshio*; Okuda, Taichi*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 P
P studied by soft X-ray photoemission spectroscopy
studied by soft X-ray photoemission spectroscopyKawasaki, Ikuto; Kobata, Masaaki; Fujimori, Shinichi; Takeda, Yukiharu; Yamagami, Hiroshi; Hedo, Masato*; Nakama, Takao*; Onuki, Yoshichika*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 RhSi
RhSiShamoto, Shinichi; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Yamauchi, Hiroki; Balakrishnan, G.*; Chang, L.-J.*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 O+
O+ Np reaction
Np reactionNishio, Katsuhisa; Vermeulen, M. J.*; Hirose, Kentaro; Kean, K. R.*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Orlandi, R.; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Tsekhanovich, I.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Ishizaki, Shoma*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Miyashita, Konan*; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
To measure the kinetic energy of a recycling muon, we discussed how to reduce the background radiation and the trajectory of the transported recycling muons by simulation code.
Nakashima, Ryota*; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
To detect a recycling muon emitted after muon catalyzed fusion reaction, it is necessary to guide the recycling muons from the target to a detector in a low background area. In this work, we simulated the muon transportation using SIMONS and PHITS codes and designed an experimental system.
Meigo, Shinichiro
no journal, ,
A high-intensity proton beam transport facility (3NBT) at J-PARC provides the proton beam accelerated at 3 GeV synchrotron accelerator to the neutron source facility and muon facility installed at the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) supplying the secondary beam of neutron and muons to the users. A talk regarding the development of the instruments for high-intensity beam transport, and the beam flattening technology based on nonlinear beam optics will be given at the annual meeting of the Physical Society of Japan,
 rays in
rays in  U(n
U(n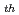 ,f)
,f)Makii, Hiroyuki; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Hirose, Kentaro; Orlandi, R.; Leguillon, R.*; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Soldner, T.*; Hambsch, F.-J.*; Frost, R. J. W.*; Tsekhanovich, I.*; et al.
no journal, ,
We have measured  rays accompanied by the
rays accompanied by the  U(n
U(n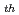 ,f) reaction in the
,f) reaction in the  -ray energy region up to about 20 MeV at the PF1b cold-neutron beam facility of the Institut Laue-Langevin (ILL), Grenoble, France. The obtained spectra exhibit local bump structures. The origins of these bump structures will be discussed using statistical model calculations.
-ray energy region up to about 20 MeV at the PF1b cold-neutron beam facility of the Institut Laue-Langevin (ILL), Grenoble, France. The obtained spectra exhibit local bump structures. The origins of these bump structures will be discussed using statistical model calculations.
 RhSi determined by magnetic PDF analysis
RhSi determined by magnetic PDF analysisKodama, Katsuaki; Honda, Takashi*; Yamauchi, Hiroki; Shamoto, Shinichi*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Otomo, Toshiya*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Fuchi, Aoi*; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*; Harada, Hiroyuki; Saha, P. K.; Shibata, Takanori*; Kinsho, Michikazu
no journal, ,
In high-intensity proton accelerator, accelerated H beams in linac are injected with charge exchange in the ring by using carbon foil. This scheme is destructive-type method by using the foil and can accumulate high intensity proton beam. However, the uncontrolled beam losses by scattering at the foil and the foil breaking by the beam collision are a key issue of high-intensity proton accelerator in the world. In the J-PARC, we newly propose a laser stripping injection scheme of nondestructive-type method as an alternative to the foil and are under development for a proof-of-principle experiment of the method. We developed laser system and optical cavity and started the first trial of the experiment. As this experimental result, we realized the charge exchange of 0.57% for final goal one of 99%. In our presentation, developed laser system and optics will be explained and we will report first results of the experiment.
beams in linac are injected with charge exchange in the ring by using carbon foil. This scheme is destructive-type method by using the foil and can accumulate high intensity proton beam. However, the uncontrolled beam losses by scattering at the foil and the foil breaking by the beam collision are a key issue of high-intensity proton accelerator in the world. In the J-PARC, we newly propose a laser stripping injection scheme of nondestructive-type method as an alternative to the foil and are under development for a proof-of-principle experiment of the method. We developed laser system and optical cavity and started the first trial of the experiment. As this experimental result, we realized the charge exchange of 0.57% for final goal one of 99%. In our presentation, developed laser system and optics will be explained and we will report first results of the experiment.
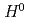 atoms generated by laser
atoms generated by laser 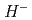 stripping
strippingShibata, Takanori*; Harada, Hiroyuki; Saha, P. K.; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*; Fuchi, Aoi*; Kinsho, Michikazu
no journal, ,
In order to further increase the intensity of the proton beam at J-PARC, we are planning a laser charge conversion test to convert the proton beam to protons nondestructively instead of the current carbon film. In the laser charge conversion process, we are considering a scenario in which neutral hydrogen 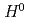 is passed through excited
is passed through excited 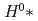 . For this experiment, it is necessary to understand the energy levels of
. For this experiment, it is necessary to understand the energy levels of 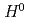 and its excitation efficiency. In this study, we are developing a spectroscopic measurement system to spectroscopically detect the light emitted from the excited
and its excitation efficiency. In this study, we are developing a spectroscopic measurement system to spectroscopically detect the light emitted from the excited 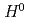 . In this presentation, we will report on the development of the spectroscopic measurement system, which is important for laser charge conversion.
. In this presentation, we will report on the development of the spectroscopic measurement system, which is important for laser charge conversion.
Chimura, Motoki; Harada, Hiroyuki; Moriya, Katsuhiro; Okabe, Kota; Kinsho, Michikazu
no journal, ,
High intensity beam also increases the beam loss, which originates from the space charge effect, so that the intensity is limited from the maintenance point of view. In the early acceleration region where the space charge field is very strong, its nonlinearity causes a rapid emittance increase over a short distance. Although this emittance growth has a small effect on the activation at that point, it causes an increase in the beam loss after that point. In this study, we propose a new method to suppress this emittance growth by compensating the nonlinear term of the space charge field by inducing a nonlinear octupole magnetic field, and perform a beam simulation of the J-PARC linac model using the IMPACT. As a result, it was confirmed that the expansion of the beam distribution in the outer core and the beam loss was suppressed. In this presentation, the results of the space charge compensation will be reported and the experimental plan will be discussed.
Idomura, Yasuhiro; Obrejan, K.*; Asahi, Yuichi; Honda, Mitsuru*
no journal, ,
Transport mechanisms of tracer impurities in the ion temperature gradient driven (ITG) turbulence are studied using the global full-f gyrokinetic code GT5D, and it is found that neoclassical particle transport is greatly enhanced by an interaction with the ITG turbulence. The radial electric field grows by turbulent bulk particle transport driven by the ITG turbulence. A compression effect of the resulting E B flows generates up-down asymmetric density perturbations, which are coupled with the magnetic drift to enhance neoclassical particle transport. This effect does not work for the temperature, and selectively enhances only particle transport.
B flows generates up-down asymmetric density perturbations, which are coupled with the magnetic drift to enhance neoclassical particle transport. This effect does not work for the temperature, and selectively enhances only particle transport.
Yanai, Kyosuke; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Otani, Masashi*; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hirano, Koichiro; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Moriya, Katsuhiro
no journal, ,
Currently, in the J-PARC linac, the emittance growth of 20 to 30% between the radio frequency linac (RFQ) and drift tube linac (DTL) in an large issue. The mismatch into the DTL is a candidate of the reason and precise beam measurement at the medium energy beam transport (MEBT) is necessary. The emittance and twiss parameters are now measured using Q-scan method, but the systematic error of this measurement is not yet fully evaluated. To this end, the measured emittance with Q-scan method and that with double-slit type emittance scanner should be compared to evaluate the measurement accuracy. We conducted this measurement at an RFQ test stand. Currently, there are difference of 2-3 mm between the measured profile and the simulation. The RFQ simulation needs to be reconsidered. The beam based alignment of the beam profile monitor has been performed also. The difference of 1mm between the magnetic and BPM center is observed, and the reason is under investigation. In this paper, these beam measurements are described.
Tajima, Minori*; Takamine, Aiko*; Iimura, Hideki; Wada, Michiharu*; Schuessler, H. A.*; Ueno, Hideki*
no journal, ,
Collinear laser spectroscopy is widely used to measure the isotope shifts and the hyperfine structures of unstable nuclei, from which the change of charge radii and the electromagnetic moments of these nuclei are deduced. However, radioisotopes of refractory elements have not been measured, because it is difficult to generate the ion beams necessary for collinear laser spectroscopy. Recently, SLOWRI has been constructed at RIKEN RI beam facility (RIBF), which can afford the ion beams of radioisotopes of all elements. We are developing a collinear laser spectroscopy setup at SLOWRI. We have confirmed that the reference values of the isotope shifts and the hyperfine structure constants of stable Ba isotopes were obtained. Since the intensities of radioisotopes are much lower than those of stable isotopes, improvement of sensitivity by using such as ion-photon coincidence is now in progress.